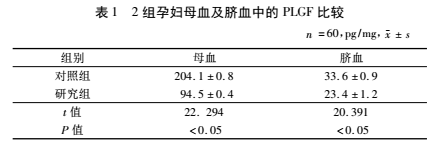
Maternal blood and cord blood of pregnant women in fetal growth restriction group
PLGF concentration is lower than normal pregnancy group
The concentration of PLGF in the maternal blood and cord blood of pregnant women in the fetal growth restriction group (study group) was significantly lower than that in the normal pregnancy group (control group), and the difference was statistically significant. See Table 1.

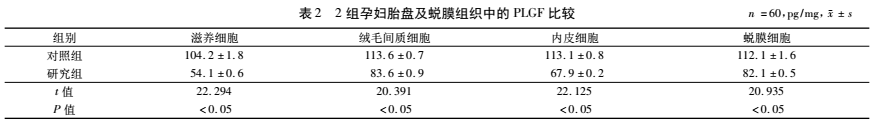
Placenta and decidua tissues of pregnant women in the fetal growth restriction group
PLGF expression is lower than normal pregnancy group
The expression of PLGF in the placenta and decidua tissues of pregnant women in the fetal growth restriction group (study group) was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. See Table 2.

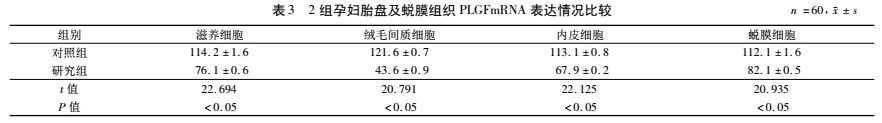
Placenta and decidual tissues of pregnant women in the fetal growth restriction group
The expression of PLGF mRNA was lower than that of the normal pregnancy group
The expression of PLGF mRNA in the placenta and decidua tissues of pregnant women in the fetal growth restriction group (research group) was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. See Table 3.

PLGF is essentially a protein, and it is a kind of heparin-binding acidic protein. This factor exists in normal human body. It is transcribed, translated and expressed in mesenchymal cells and then released outside the cell, but it is released at this time. Factors are inactive and need to be processed. Under the action of proteolytic enzymes, a 69kDa chain and 34kDI3 chain are connected by disulfide bonds to form related dimers, so they are active.
PLGF can not only promote the growth and development of placental cells, but also promote the growth of vascular endothelial cells, which is conducive to the formation of the vascular system of the fetus, thereby promoting the growth and development of the fetus.The base sequence of PLGF is basically the same as the base sequence of VEGF, and it binds to specific receptors in the placenta to perform biological functions and jointly promote the development of the fetus. PLGF can to a certain extent promote the proliferation and differentiation of trophoblast cells in women during early pregnancy, and further invade and lead to the proliferation, differentiation, migration and activation of endothelial cells, thereby increasing the permeability of blood vessels and effectively enhancing the biological activity of low concentrations of VEGF , Anti-apoptosis of endothelial cells.
In the process of placenta formation in normal pregnant women, PLGF plays a great role in promoting the growth and development of placental cells, thereby promoting the growth and development of the fetus. This study found that the concentration of PLGF in the cord blood of pregnant women in the study group was significantly lower than that in the control group, indicating that intrauterine growth would first seriously affect the expression of placental growth factor in pregnant women, which is consistent with related studies.
PLGF and fetal growth restriction
(fetal growth restriction, FGR) relevance
FGR not only seriously affects the development of the fetus, but also affects the development of the fetus in the future childhood and adolescence. It is one of the important complications of the perinatal period. The cause of FGR has been studied abroad for a long time, but the specific cause has not yet been clearly explained. When the fetus is facing growth restriction, the villi in the placenta are underdeveloped and the blood vessels of the villi are not fully expanded, which directly leads to poor perfusion of the placenta in the uterus of the pregnant woman, causing chronic hypoxia in the uterus, and seriously affecting the growth of the fetus. development.PLGF has many functions. It can promote the growth and development of placental cells in the early stage of pregnant women, cause endothelial cells to divide and proliferate, thereby increasing the permeability of blood vessels and allowing children to fully absorb nutrients.
Relevant studies have shown that the expression levels of growth factors are different in different cells and tissues. Among them, it is most expressed in the placenta, which in turn contributes to the growth and development of the placenta. The expression of PLGF in the placenta and decidua tissues of pregnant women in the study group was significantly lower than that in the control group. The expression of PLGF mRNA in the placenta and decidua tissues of pregnant women in the study group was significantly lower than that in the control group.
FGR is a disease that occurs frequently among pregnant women during the perinatal period. This disease will seriously affect the growth and development of the fetus, as well as the physical and mental health and quality of life of pregnant women. Relevant studies have found that intrauterine FGR can cause a series of inflammations, such as placental villus dysplasia, inadequate expansion of placental villi, and poor expansion of spiral arteries in the decidual tissue, which in turn makes the blood flow in the uterus placenta blocked and the fetus cannot Adequate absorption of nutrients such as stunted growth. The semi-quantitative results of PLGF mRNA in the placenta and decidua of the two groups showed that the expression of PLGF mRNA in the placenta and decidua of the study group was lower than that in the control group.
In summary, PLGF has conducted research on the correlation of placental intrauterine growth restriction, on the one hand, it has been found that PLGF has an important role in the pathogenesis of FGR, on the other hand, it can be diagnosed and treated sequentially.It is worthy of clinical promotion and application.












